EXPLORING ACCESS
1. WORKING WITH ACCESS
A database is any collection of related data organized for fast search and retrieval.
For example, a telephone book is a non-computerized database of information. It is
organized in alphabetical order and includes information such as names,
addresses, and telephone numbers. Other examples of non-computerized
databases include address books and inventory lists
Data is raw, unorganized facts and details. Examples of data that could be stored
in a database are:
A student’s test score
- • An employee’s ID
- • A vendor’s email address.
Information is the processed output of data. It provides context for data. Examples are:
- • Average test score per subject chart
- • Mailing list sorted alphabetically and organized by location.
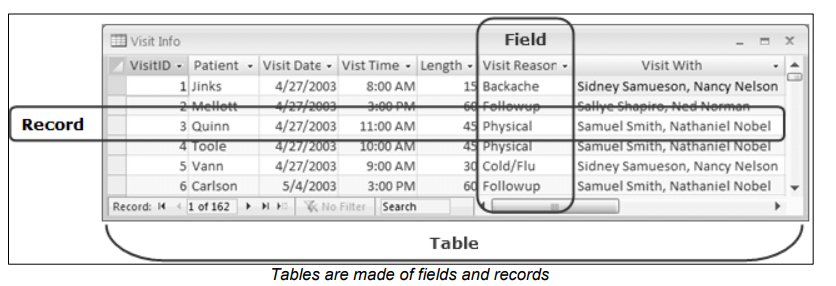
In Microsoft Access 2010, the database information is stored in data tables.
Every data table has a structure that provides for the collection, organization,
storage, and retrieval of data. These tables of information are contained in a
database file. Each database file can have numerous data tables.
Some of the common uses of large-scale databases are:
Airline booking systems:
These systems maintain a database of all the seats on all the available
flights, allowing passengers to be quickly booked onto flights to their
destination.
Government records: Governments all over the world rely on multiple large databases in order to function. Tax records, criminal records, and social security all require sophisticated database systems.
Bank account records: Banks require extremely reliable databases in order to keep track of all their customer account and log transactions.
Hospital patient details:
Medical records are stored in a database system. This system should allow
your medical history to be instantly available wherever you require
treatment.
Access is a tool that you can use to quickly and easily develop relational database applications that help you manage information. You can create a database to help you keep track of just about any kind of information, such as inventory, professional contacts, or business processes. In fact, Access comes with templates that you can use right away to track a variety of information, making things easy even for a beginner.
Professional databases are designed and created by database specialists. These are highly skilled database professionals with an in-depth knowledge of exactly how the database works, including its overall function and details programming. Database specialists design and create databases to meet the organization’s needs for present and future use.
For example, a database specialist analyses the data processing and information needs of a computer training center and designs a database that allows the storing of students, trainers, and course details.
There are various roles that are assigned to maintain the database, such as:
1. Database administrator:
a) Controls access to different data for specific users.
b) Implements security measures to safeguard the organization’s database.
c) Has overall responsibility for the maintenance and repair of an organization’s database.
d) Recovers the database after a crash or major errors.
2. Database user:
a) Enters, updates, and retrieves data/information.
b) Granted access rights as needed for basic data entry and search.
For example, a database administrator assigns various access permission to data entry personnel, course administrators, and managers for the database in the computer training center. Data entry personnel may only enter and edit student records but cannot access trainers or course details. The database administrator may incorporate password protection for sensitive data in the database.
A database user in the computer training center can access the database based
on the access level granted. Data entry personnel can only enter/edit/search/print records of students but cannot access trainer details. Managers may have a higher
level of access such as can view/editing/search/printing records and reports of students,
trainers, and courses.