3.2 COMPUTER HARDWARE
| Site: | UNITE LMS |
| Course: | COMPUTER BASIC SKILLS |
| Book: | 3.2 COMPUTER HARDWARE |
| Printed by: | Guest user |
| Date: | Wednesday, 4 February 2026, 4:26 PM |
Description
Click on the link above to access this material, this module covers the following units;
- INPUT DEVICES
- OUTPUT DEVICES
- STORAGE DEVICES
- PROCESSING DEVICES
1. Introduction To Computer Hardware
 Computer hardware refers to all the tangible components of the computer system. Every time, new devices are invented and used for different purposes.
Computer hardware refers to all the tangible components of the computer system. Every time, new devices are invented and used for different purposes.
Computer hardware equals the collection of physical elements that comprise a computer system. Computer hardware refers to the physical parts or components of a computer such as a monitor, keyboard, hard drive disk, mouse, printers, graphic cards, sound cards, memory, motherboard, chips, etc. all of which are physical object that you can actually touch.
2. INPUT DEVICES
UNIT INTRODUCTION
Input devices are used to enter data or commands in a form that the computer can
use. They send the data or commands to the processing unit. According to the type of
data they input, they can be grouped into the following:
- Text input devices
- Pointing Input Devices
- Imaging input Devices
- Gaming input Devices
- Audio input Devices
- Biometric input Devices
- And Other Specialized input devices.
A. TEXT INPUT DEVICES
Text is a general word for all characters such as letters, numerical digits, symbols, and marks that combine to form words, sentences, paragraphs, and so on. Text input devices are all the devices that are used for entering text into the computer. There is a variety of devices that help us to input text into a computer.
Text input devices include:
The Keyboard,
- Voice Recognition Equipment
- OMR and Barcode readers
- OCR and Optical readers
- MICR readers
- RFID readers
- Magnetic Strip Card Readers, etc
1. THE KEYBOARD
Definition: A keyboard is an input device, consisting of a set of keys used to
operate a computer. Each press of a key corresponds to a single written character of text, but to produce
some symbols requires pressing and holding several keys simultaneously. Usually, a standard keyboard has between 80 and 110 keys. A keyboard is the main and most reliable computer input device. The QWERTY is referred to as the "Universal" keyboard.
The name "QWERTY" comes from the first six letters in the top alphabet row (the one just below the numbers). There are other setups also available such as Dvorak, ABCDE, GKOS, QWERTZ, and AZERTY Keypads, Keyers and chorded keyboards have fewer keys, specially designed for devices such as pocket-sized computers. Christopher Latham Sholes was an American newspaper publisher. In 1866, he invented the first practical typewriter and the
QWERTY keyboard layout is still in use today.
ADVANTAGES OF KEYBOARD
- Keyboards are very common (commonly supplied with computers)
- Entering data and commands with the keyboard is faster than compared to the mouse
- Keyboards are more reliable
DEMERITS OF KEYBOARD
- It takes a lot of time to practice in order to type quickly
- Keys can easily become faulty due to dust.
- Some keyboards keys are very hard to press, causing fingers to hurt.
2. VOICE RECOGNITION EQUIPMENT
Voice Recognition Equipment (Speech recognition) converts spoken words to text. Computers with Speech recognition do not actually understand speech, but they are programmed to recognize a vocabulary of words, which can range from two words to millions of words.
ADVANTAGES
- No typing of data is necessary.
- Voice recognition can be used by people whose hands are disabled.
- Dictating text is faster than typing.
- Voice Recognition systems are also ideal for the blind.
DEMERITS OF TEXT INPUT BY SPEECH RECOGNITION
- The error rate is high, depending on the user’s accent.
- Words with the same pronunciations (Homophones) like see and sea cannot be distinguished
- Speech Recognition does can’t work in a noisy environment
- The Voice Recognition software must be trained to recognize more words.
- It requires the user to speak in a writing style, i.e. even
- pronouncing the marks such as commas.
OPTICAL MARK RECOGNITION (OMR)
 Optical mark recognition (OMR) devices read hand-drawn marks such as small circles or rectangles. A person places these marks on a form, such as a test, survey, or questionnaire answer sheet. The OMR device first reads a master document, such as an answer key sheet for a test, to record correct answers based on patterns of light; the remaining documents then are passed through the OMR device and their patterns of light are matched against the master document.
Optical mark recognition (OMR) devices read hand-drawn marks such as small circles or rectangles. A person places these marks on a form, such as a test, survey, or questionnaire answer sheet. The OMR device first reads a master document, such as an answer key sheet for a test, to record correct answers based on patterns of light; the remaining documents then are passed through the OMR device and their patterns of light are matched against the master document.
4. BARCODE READERS
 A bar code reader is an optical reader that uses laser beams to read bar codes that are printed on items
A bar code reader is an optical reader that uses laser beams to read bar codes that are printed on items
usually in supermarkets. A bar code is an identification code that normally consists of a set of vertical lines
and spaces of different widths. The bar code represents some data that identifies the item and the manufacturer.
5. OPTICAL CHARACTER RECOGNITION (OCR)
Optical character recognition (OCR) is a technology that involves reading typewritten, computer-printed, or handwritten characters from ordinary documents and translating the images into a form that the computer can
understand. OCR devices include a small optical scanner for reading characters and sophisticated software (OCR software) for analyzing what is read.
6. MICR READERS
 Magnetic-ink character recognition (MICR) reader is used to read text printed with magnetized ink.
Magnetic-ink character recognition (MICR) reader is used to read text printed with magnetized ink.
MICR readers are mainly used by the banking industry for processing checks. Each check is inserted into a MICR reader, which sends the check information to a computer for processing.
2.1. IMAGING DEVICES
Imaging input Devices are devices that input images such as still photos, motion pictures, graphics, video, etc. into the computer for processing. Common Imaging devices include:
- Image scanner
- Digital Camera
- Digital video (DV) camera
- Camcorder
- Webcam
1. IMAGE SCANNER
 A scanner is a light-sensing input device that converts hardcopy documents, drawings, or pictures to an electronic version (softcopy), which can then be stored on a disk. The electronic version of scanned material is in the form of rows and columns of dots called a bitmap. Each dot on a bitmap consists of one or more bits of data. Common types of scanners include:
A scanner is a light-sensing input device that converts hardcopy documents, drawings, or pictures to an electronic version (softcopy), which can then be stored on a disk. The electronic version of scanned material is in the form of rows and columns of dots called a bitmap. Each dot on a bitmap consists of one or more bits of data. Common types of scanners include:
- Flatbed scanner
- Pen or handheld scanner
- Sheet bed scanner
- Drum scanner.
2. WEBCAM
 A Webcam also called a PC video camera, is a type of digital video camera that usually sits on top of the monitor. Some laptop computers have built-in Webcams. Webcams enable users to;
A Webcam also called a PC video camera, is a type of digital video camera that usually sits on top of the monitor. Some laptop computers have built-in Webcams. Webcams enable users to;
- capture video and still images,
- send e-mail messages with video attachments
- add live images to instant messages,
- broadcast live images over the Internet, and
- make video telephone calls.
3. DIGITAL CAMERA
 A digital camera allows users to take pictures and store the photographed images digitally instead of storing them on a traditional film. When you take pictures, the images are electronically stored in the camera. Later, you transfer a copy of the stored pictures to your computer or printer by connecting a cable between the digital camera and your computer.
A digital camera allows users to take pictures and store the photographed images digitally instead of storing them on a traditional film. When you take pictures, the images are electronically stored in the camera. Later, you transfer a copy of the stored pictures to your computer or printer by connecting a cable between the digital camera and your computer.
4. DIGITAL VIDEO (DV) CAMERA
A digital video (DV) camera, by contrast, records video as digital signals instead of analog signals. To transfer recorded images to the computer hard disk, users connect DV cameras directly to a port on the system unit. After saving the video on a storage medium, you can play it or edit it and burn it to a DVD using software programs on the computer.
5. CAMCORDER
 This is a lightweight easily portable video camera that records data in digital form onto a storage device such as a hard disk or a videotape.
This is a lightweight easily portable video camera that records data in digital form onto a storage device such as a hard disk or a videotape.
2.2. AUDIO INPUT DEVICES
Audio input is the process of entering any sound into the computer such as speech, music, and sound effects. To enter sound into a computer, it must have a sound card. Audio input devices are plugged into a port on the sound card. Examples of audio input devices include;
- Microphones,
- Tape players,
- CD/DVD players,
- MIDI devices
- Dictaphone, etc.
1. MICROPHONES
 A microphone is an instrument for converting sound waves into electrical energy variations, which may then input into the computer for processing, recording or audio playback. Various types of Microphones available. Microphones are connected to the sound card in the system unit.
A microphone is an instrument for converting sound waves into electrical energy variations, which may then input into the computer for processing, recording or audio playback. Various types of Microphones available. Microphones are connected to the sound card in the system unit.
2. MIDI DEVICES
 MIDI (musical instrument digital interface) is the standard that defines how digital musical devices represent sound electronically. MIDI devices such as electronic pianos allow users to record and edit music e.g. you can set the beat speed, and add notes, to produce sound.
MIDI (musical instrument digital interface) is the standard that defines how digital musical devices represent sound electronically. MIDI devices such as electronic pianos allow users to record and edit music e.g. you can set the beat speed, and add notes, to produce sound.
3. DICTAPHONE
 This is the earliest device most commonly used to record speech for later playback or to be typed into print. It was established by Alexander Graham Bell in Washington, D.C. in 1881.
This is the earliest device most commonly used to record speech for later playback or to be typed into print. It was established by Alexander Graham Bell in Washington, D.C. in 1881.
2.3. GAMING INPUT DEVICES
Gaming input devices are devices specifically designed to be used for playing computer games.
Examples Include:
- Gaming Keyboard
- Joysticks and wheels
- Gamepad
- The light guns Dance pad
- Motion sensing game controllers
1. GAMING KEYBOARD
 Gaming keyboards typically include programmable keys so that gamers can customize the keyboard to the game being played. The keys on gaming keyboards light up so that the keys are visible in all lighting conditions. Some have small displays that show important game statistics, such as time to targets
Gaming keyboards typically include programmable keys so that gamers can customize the keyboard to the game being played. The keys on gaming keyboards light up so that the keys are visible in all lighting conditions. Some have small displays that show important game statistics, such as time to targets
remaining.
2. GAMING WHEELS
 A gaming wheel is a steering wheel-type input device. Users turn the wheel to simulate driving a vehicle using programs on a computer. Most gaming wheels also include foot pedals for acceleration and braking actions.
A gaming wheel is a steering wheel-type input device. Users turn the wheel to simulate driving a vehicle using programs on a computer. Most gaming wheels also include foot pedals for acceleration and braking actions.
Gaming wheels include buttons, called triggers that you press to initiate certain events.
3. JOYSTICK
 Joystick- Consists of a stick that pivots on a base and reports its angle or direction to the device it is controlling. Joysticks are often used to control video games, and usually have one or more push- buttons whose state can also be read by the computer. Joysticks can also be used as pointing devices.
Joystick- Consists of a stick that pivots on a base and reports its angle or direction to the device it is controlling. Joysticks are often used to control video games, and usually have one or more push- buttons whose state can also be read by the computer. Joysticks can also be used as pointing devices.
4. GAMEPAD
 A gamepad controls the movement and actions of players or objects in video games or computer games. On the gamepad, users press buttons with their thumbs or move sticks in various directions to trigger events. Gamepads communicate with a game console or a personal computer via wired or wireless technology.
A gamepad controls the movement and actions of players or objects in video games or computer games. On the gamepad, users press buttons with their thumbs or move sticks in various directions to trigger events. Gamepads communicate with a game console or a personal computer via wired or wireless technology.
5. LIGHT GUNS
 A light gun is used to shoot targets and moving objects after you pull the trigger on the weapon. Instead of emitting light, most light guns work by detecting light. When the user pulls the trigger, the screen uses one of several techniques to send light, which is received by a receptor in the barrel of the gun.
A light gun is used to shoot targets and moving objects after you pull the trigger on the weapon. Instead of emitting light, most light guns work by detecting light. When the user pulls the trigger, the screen uses one of several techniques to send light, which is received by a receptor in the barrel of the gun.
6. DANCE PAD
 A dance pad is a flat electronic device divided into panels that users press with their feet in response to instructions from a music video game. These games test the user’s ability to step on the correct panel at the correct time, following a pattern that is matching with the beat of a song.
A dance pad is a flat electronic device divided into panels that users press with their feet in response to instructions from a music video game. These games test the user’s ability to step on the correct panel at the correct time, following a pattern that is matching with the beat of a song.
7. MOTION-SENSING GAME CONTROLLERS
 These are devices that allow the user to guide onscreen elements by moving a handheld input device in predetermined directions through the air. Examples include the power glove, and play station move gadgets, among others.
These are devices that allow the user to guide onscreen elements by moving a handheld input device in predetermined directions through the air. Examples include the power glove, and play station move gadgets, among others.
watch the video below to appreciate how Joysticks and Gamepads are used
2.4. BIOMETRIC INPUT DEVICES
A biometric device translates a biological personal characteristic into a digital code that is stored or compared with a digital code stored in the computer. Common biometric devices include:
- Fingerprint scanner
- Face Recognition systems
- Hand geometry systems
- Signature verification systems
- Iris Recognition systems
1. FINGERPRINT SCANNER
 A fingerprint scanner captures the curves and indentations of a fingerprint. Some grocery and retail stores now use fingerprint readers as a means of payment, where the customer's fingerprint is linked to an account or credit card.
A fingerprint scanner captures the curves and indentations of a fingerprint. Some grocery and retail stores now use fingerprint readers as a means of payment, where the customer's fingerprint is linked to an account or credit card.
2. FACE RECOGNITION SYSTEMS
 A face recognition system captures a live face image and compares it with a stored image to determine if the person is a legitimate user. Some buildings use face-recognition systems to secure access to rooms.
A face recognition system captures a live face image and compares it with a stored image to determine if the person is a legitimate user. Some buildings use face-recognition systems to secure access to rooms.
3. HAND GEOMETRY SYSTEM
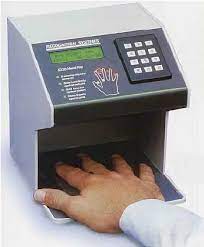 Biometric devices measure the shape and size of a person's hand using a hand geometry system. Some large companies use this system as time and attendance devices or as security devices. Day-care centers use this system to verify parents who pick up their children.
Biometric devices measure the shape and size of a person's hand using a hand geometry system. Some large companies use this system as time and attendance devices or as security devices. Day-care centers use this system to verify parents who pick up their children.
4. SIGNATURE VERIFICATION SYSTEMS
 A signature verification system recognizes the shape of your handwritten signature, as well as measures the pressure exerted and the motion used to write the signature. The signature verification system uses a specialized pen and tablet.
A signature verification system recognizes the shape of your handwritten signature, as well as measures the pressure exerted and the motion used to write the signature. The signature verification system uses a specialized pen and tablet.
5. IRIS RECOGNITION SYSTEM
 These are devices that use iris recognition technology to read patterns in the iris of the eye. These patterns are as unique as a fingerprint. Iris recognition systems are used by government security organizations, the military, and financial institutions that deal with highly sensitive data.
These are devices that use iris recognition technology to read patterns in the iris of the eye. These patterns are as unique as a fingerprint. Iris recognition systems are used by government security organizations, the military, and financial institutions that deal with highly sensitive data.
3. OUTPUT DEVICES
INTRODUCTION
Output is data that has been processed into a useful form called information. Computers generate several types of output, depending on the hardware and software being used and the requirements of the user.
An output device is any type of hardware component capable of conveying information to one or more people. Commonly used output devices include display devices, printers, Audio Output Devices, and others.
3.1. CATEGORIES OF COMPUTER OUTPUT
While working with a computer, a user encounters four basic categories of output:
- Text, (characters that are used to create words, sentences, and paragraphs)
- Graphics (non-text information such as drawings and charts),
- Audio(music, speech, or any other sound)
- Video (full-motion images played back at various speeds)
3.2. DISPLAY COMPUTERS
PRINTERS
 A printer is a device that produces a hard copy output such as text and graphics on a physical material like paper.
A printer is a device that produces a hard copy output such as text and graphics on a physical material like paper.
Printed information (hard copy) exists physically and in a more permanent form than a soft copy on a display device. Printers with different speeds, features, quality, and capabilities are available at a range of prices. Printers can be grouped into two categories: impact and nonimpact printers.
IMPACT PRINTERS
 An impact printer forms characters and graphics on a piece of paper by a striking mechanism against an ink ribbon that physically contacts the paper. Impact printers are noisy because of this striking activity. Large Businesses use impact printers because these printers can withstand dusty environments, vibrations, and extreme temperatures. Commonly used types of impact printers include Daisy wheel, dot-matrix, Braille, and line printers.
An impact printer forms characters and graphics on a piece of paper by a striking mechanism against an ink ribbon that physically contacts the paper. Impact printers are noisy because of this striking activity. Large Businesses use impact printers because these printers can withstand dusty environments, vibrations, and extreme temperatures. Commonly used types of impact printers include Daisy wheel, dot-matrix, Braille, and line printers.
DAISYWHEEL PRINTER
 This is a kind of impact printer where characters are arranged on the ends of the spokes of a wheel. The wheel (usually made of plastic) is rotated to select the character to print and then an electrically operated hammer bends the selected spoke forward slightly, squeezing in an ink ribbon between the character and the paper, as in a typewriter. One advantage of this arrangement over that of a typewriter is that different wheels may be inserted to produce different typefaces (font styles and sizes) Low speed and noise are its disadvantages. The speeds are between 20 and 90 characters per second (cps).
This is a kind of impact printer where characters are arranged on the ends of the spokes of a wheel. The wheel (usually made of plastic) is rotated to select the character to print and then an electrically operated hammer bends the selected spoke forward slightly, squeezing in an ink ribbon between the character and the paper, as in a typewriter. One advantage of this arrangement over that of a typewriter is that different wheels may be inserted to produce different typefaces (font styles and sizes) Low speed and noise are its disadvantages. The speeds are between 20 and 90 characters per second (cps).
DOT-MATRIX PRINTER
 A dot-matrix printer produces printed images when tiny wire pins on a print head mechanism strike an inked ribbon like in a typewriter. When the ribbon presses against the paper, it creates dots that form characters and graphics. Most dot-matrix printers use continuous-form paper, in which thousands of sheets of paper are connected together end to end. The papers have holes along the sides to help feed the paper through the printer. Dot matrix printers provide cheap but low-quality printing.
A dot-matrix printer produces printed images when tiny wire pins on a print head mechanism strike an inked ribbon like in a typewriter. When the ribbon presses against the paper, it creates dots that form characters and graphics. Most dot-matrix printers use continuous-form paper, in which thousands of sheets of paper are connected together end to end. The papers have holes along the sides to help feed the paper through the printer. Dot matrix printers provide cheap but low-quality printing.
BRAILLE PRINTERS
 A Braille printer, commonly known as a Braille embosser, is an impact printer that renders text as
A Braille printer, commonly known as a Braille embosser, is an impact printer that renders text as
tangible dot cells which are felt and read by the blind. Using Braille translation software, a document can
be embossed with relative ease and efficiency. They need special Braille paper which is thicker and more expensive than normal paper. Once a copy is produced, printing further copies are often quicker by means of a device called a "thermoform", which produces copies on a soft plastic.
LINE PRINTERS
 A line printer is a high-speed impact printer that prints an entire line at a time. The speed of a line printer is measured by the number of lines per minute (LPM) it can print. Some line printers print as many as 3,000 LPM.
A line printer is a high-speed impact printer that prints an entire line at a time. The speed of a line printer is measured by the number of lines per minute (LPM) it can print. Some line printers print as many as 3,000 LPM.
Mainframes, servers, or networked applications, such as manufacturing, distribution, or shipping, often use line
printers.
NON-IMPACT PRINTERS
A nonimpact printer forms characters and graphics on a piece of paper without actually striking the paper. Some spray ink, while others use heat or pressure to create images. Commonly used nonimpact printers are; ink-jet printers, laser printers, thermal printers, plotters, and mobile printers.
INK-JET PRINTER An ink-jet printer forms characters and graphics by spraying tiny drops of liquid ink onto a piece of paper. Ink-jet printers produce text and graphics in both black-and-white and color on a variety of paper types & sizes. The print head mechanism in an ink-jet printer contains ink-filled print cartridges. Each cartridge has very many small ink holes or nozzles. The ink propels through a combination of the holes to form a character or image on the paper.
An ink-jet printer forms characters and graphics by spraying tiny drops of liquid ink onto a piece of paper. Ink-jet printers produce text and graphics in both black-and-white and color on a variety of paper types & sizes. The print head mechanism in an ink-jet printer contains ink-filled print cartridges. Each cartridge has very many small ink holes or nozzles. The ink propels through a combination of the holes to form a character or image on the paper.
A bubble jet printer is a type of inkjet printer in which bubbles (droplets) of ink are formed by rapid vaporization of the ink in the chamber and then propelled onto the paper.
THERMAL PRINTER
 A thermal printer generates images by pushing heated pins against a coated heat-sensitive paper. The coating turns black in the areas where it is heated, producing an image. Basic thermal printers are cheap, but the print quality is low and the images tend to fade over time. Thermal printing technology is, however, ideal for use in small devices e.g. ATM receipt printers.
A thermal printer generates images by pushing heated pins against a coated heat-sensitive paper. The coating turns black in the areas where it is heated, producing an image. Basic thermal printers are cheap, but the print quality is low and the images tend to fade over time. Thermal printing technology is, however, ideal for use in small devices e.g. ATM receipt printers.
PLOTTERS Plotters are printers used to produce large, high-quality, vector graphic drawings such as blueprints, maps, posters, and signs. These printers are usually very costly and are used in specialized fields such as engineering, and graphic art. They use ink-jet printer technology, on a much larger scale, to print professional quality displays.
Plotters are printers used to produce large, high-quality, vector graphic drawings such as blueprints, maps, posters, and signs. These printers are usually very costly and are used in specialized fields such as engineering, and graphic art. They use ink-jet printer technology, on a much larger scale, to print professional quality displays.
MOBILE PRINTERS A mobile printer is a small, lightweight, battery-powered printer that allows a mobile user to print from a notebook
A mobile printer is a small, lightweight, battery-powered printer that allows a mobile user to print from a notebook
computer, Tablet PC, PDA, smartphone, or another personal mobile device while traveling. They fit easily in a briefcase alongside a notebook computer Mobile printers mainly use ink-jet, thermal, wax-transfer, or dye-sublimation technology.
3.3. TERMS ASSOCIATED WITH PRINTERS
TERMS ASSOCIATED WITH PRINTERS
 1. Toner is a powder used in laser printers and photocopiers to form printed text and images on paper.
1. Toner is a powder used in laser printers and photocopiers to form printed text and images on paper.
2. DPI. (Dots per inch) is a measure of the number of individual dots printed in a line within the span of 1 inch (2.54 cm). The DPI value correlates with image resolution.
3. Hard copy is a permanent reproduction, in the form of a physical object, of any media suitable for direct use such as paper.
4. Page orientation is the way in which a rectangular page is focused for normal viewing. The two most common types of orientation are;
- portrait
- landscape.
A page in portrait orientation is taller than it is wide, with information printed across the shorter width of the paper.
A page in landscape orientation is wider than it is tall, with information printed across the widest part of the paper.
3.4. AUDIO OUTPUT DEVICES
AUDIO OUTPUT DEVICES
Audio output devices are the components of the computer system that produce music, speech, or other sounds, such as beeps. Common Audio Output Devices include:
- Computer Speakers
- PC Internal Speakers
- Headphones and
- Earphones
A. COMPUTER SPEAKERS
 Computer Speakers typically have tone and volume controls, allowing users to adjust settings. To boost the low bass sounds, surround sound speaker systems also include a woofer, with one or two center speakers and two or more satellite speakers that are positioned so that sound emits from all directions. Some Computer Speakers use Wireless technology.
Computer Speakers typically have tone and volume controls, allowing users to adjust settings. To boost the low bass sounds, surround sound speaker systems also include a woofer, with one or two center speakers and two or more satellite speakers that are positioned so that sound emits from all directions. Some Computer Speakers use Wireless technology.
B. PC INTERNAL SPEAKERS
 Most personal computers have small internal speakers that basically output beeps and low-quality sound.
Most personal computers have small internal speakers that basically output beeps and low-quality sound.
C. HEADPHONES AND EARPHONES
 In a crowded computer laboratory environment, speakers might not be applicable. Instead, users can plug headphones or earphones in a port on the sound card, in a speaker, or on the front of the system unit. With headphones or earphones, only the individual wearing the headset hears the sound from the computer.
In a crowded computer laboratory environment, speakers might not be applicable. Instead, users can plug headphones or earphones in a port on the sound card, in a speaker, or on the front of the system unit. With headphones or earphones, only the individual wearing the headset hears the sound from the computer.
4. PROCESSING DEVICES
 Processing devices are the computer electronic components and chips housed in the system unit. The system unit is a box-like case that houses the motherboard, the disks and drives bays, the power supply, and the cooling systems. The components in the system unit are connected to the motherboard. Two major components on the motherboard are the CPU and internal memory. A drive bay is a rectangular opening that typically holds disk drives.
Processing devices are the computer electronic components and chips housed in the system unit. The system unit is a box-like case that houses the motherboard, the disks and drives bays, the power supply, and the cooling systems. The components in the system unit are connected to the motherboard. Two major components on the motherboard are the CPU and internal memory. A drive bay is a rectangular opening that typically holds disk drives.
THE MOTHERBOARD
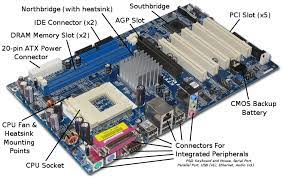 The motherboard is a single circuit board that provides the path through which the processor communicates with internal and peripheral devices. The motherboard is also called the system board. The components attached to the motherboard include the processor chip, memory chips, buses, and Expansion Slots for Adapter Cards.
The motherboard is a single circuit board that provides the path through which the processor communicates with internal and peripheral devices. The motherboard is also called the system board. The components attached to the motherboard include the processor chip, memory chips, buses, and Expansion Slots for Adapter Cards.
BUSES
 The BUS is a common electrical path that enables data flow between the various system components. A bus allows the various devices inside and attached to the system unit to communicate with each other. All buses consist of
The BUS is a common electrical path that enables data flow between the various system components. A bus allows the various devices inside and attached to the system unit to communicate with each other. All buses consist of
two parts:
- The data bus which transfers actual data bits and
- The address bus transfers information about where the data should go in memory.
EXPANSION SLOTS AND ADAPTER CARDS
 An expansion slot is a socket on the motherboard that can hold an adapter card. An adapter card also called an expansion card, is a circuit board that increases the capabilities of the system or provides connections to peripherals. Some motherboards include all necessary capabilities and do not require adapter cards. Adapter cards are used for many supplemental capabilities, such as more memory, higher quality sound devices, a modem, extra ports, or graphics capabilities.
An expansion slot is a socket on the motherboard that can hold an adapter card. An adapter card also called an expansion card, is a circuit board that increases the capabilities of the system or provides connections to peripherals. Some motherboards include all necessary capabilities and do not require adapter cards. Adapter cards are used for many supplemental capabilities, such as more memory, higher quality sound devices, a modem, extra ports, or graphics capabilities.