STARTING EXCEL 2016
| Site: | UNITE LMS |
| Course: | COMPUTER BASIC SKILLS |
| Book: | STARTING EXCEL 2016 |
| Printed by: | Guest user |
| Date: | Wednesday, 4 February 2026, 6:11 PM |
1. STARTING EXCEL 2013
Concepts
Microsoft Excel is a spreadsheet application developed by Microsoft for Microsoft Windows and Mac OS X. It allows you to enter numerical values or data into the rows or columns of a spreadsheet, and use these numerical entries for calculations, graphs, and statistical analysis.
Steps
To start Microsoft Excel 2013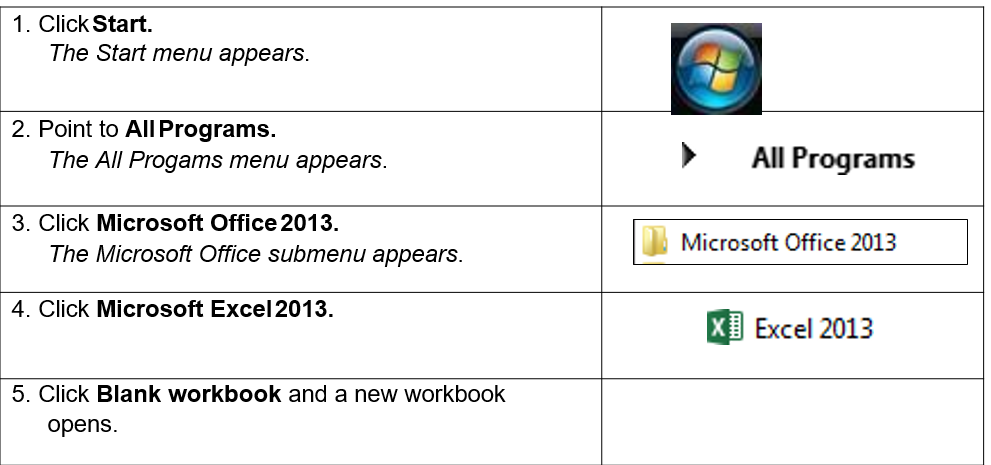
THE USER INTERFACE
Concepts
The Microsoft Excel 2013 user interface uses ribbons and tabs just like its predecessor, Microsoft Office 2010. The user interface itself has been tweaked, with changes like blocky worksheet tabs and capitalized ribbon tab names ‒ e.g., "HOME" instead of "Home." Now, you can share your files via e-mail or online.
You can also export your file to create a PDF/XPS document.
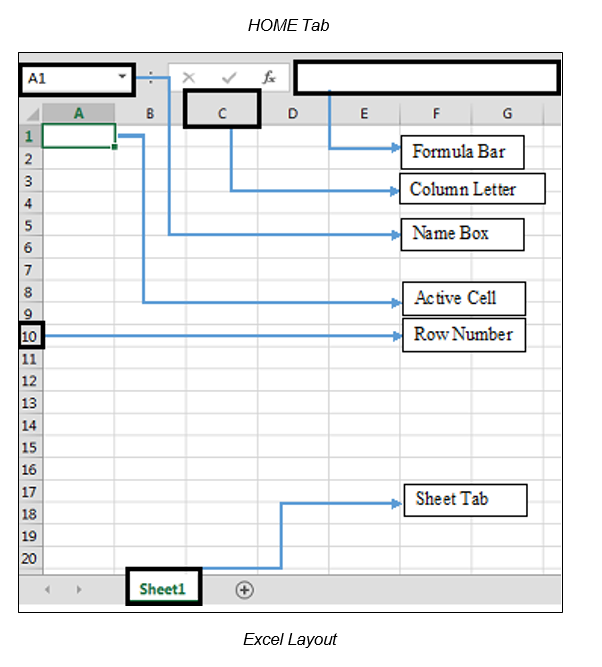
Active Cell
In an Excel 2013 worksheet, an active cell is a cell with a black outline. Data is always entered into the active cell.
Column Letter
Columns run vertically on a worksheet and each column is identified by a letter in the column header.
Formula Bar
Located above the worksheet, this area displays the contents of the active cell. It can also be used for entering or editing data and formulas.
Name Box
Located left to the formula bar, the Name Box displays the cell reference or the name of the active cell.
Row Numbers
Rows run horizontally in a worksheet and are identified by a number in the row header. Together a column letter and a row number create a cell reference. Each cell in the worksheet can be identified by this combination of letters and numbers such as A1, F456, or AA34.
Sheet Tabs
By default, there is one worksheet in an Excel file. The tab at the bottom of a worksheet tells you the name of the worksheet - such as Sheet1, Sheet2, etc.
Quick Access Toolbar
This customizable toolbar allows you to add frequently used commands. Click on the down arrow at the end of the toolbar to display the available options.
Application Button
Clicking on the Application Button displays a drop-down menu containing a number of options, such as open, save, and print. The options in the Button menu are very similar to those found under the File menu in previous versions of Excel.
Ribbon
The Ribbon is the strip of buttons and icons located above the work area in Excel 2013. The Ribbon replaces the menus and toolbars found in earlier versions of Excel.
Steps
To enter a user name:
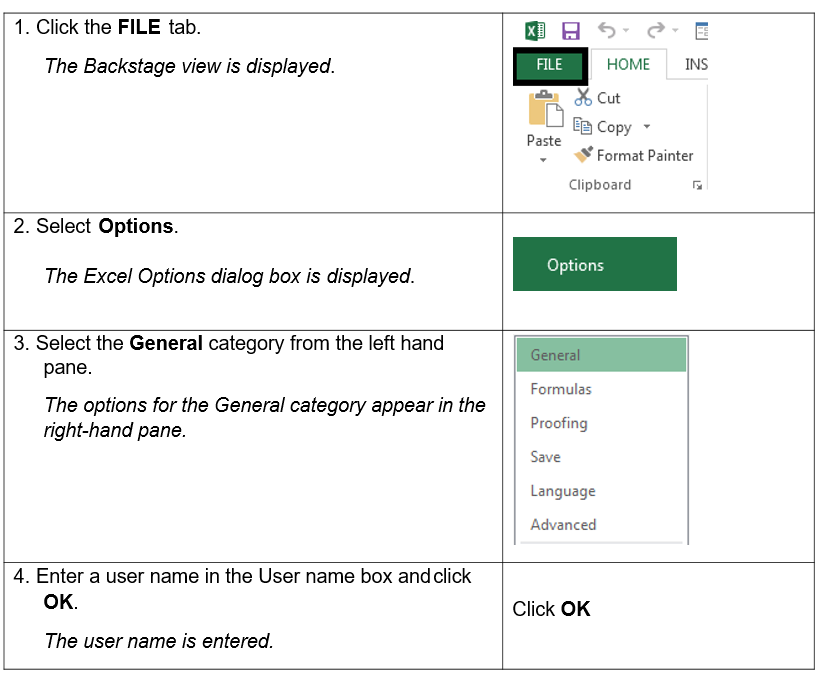
Steps
To enter a default file location from which to open and save spreadsheets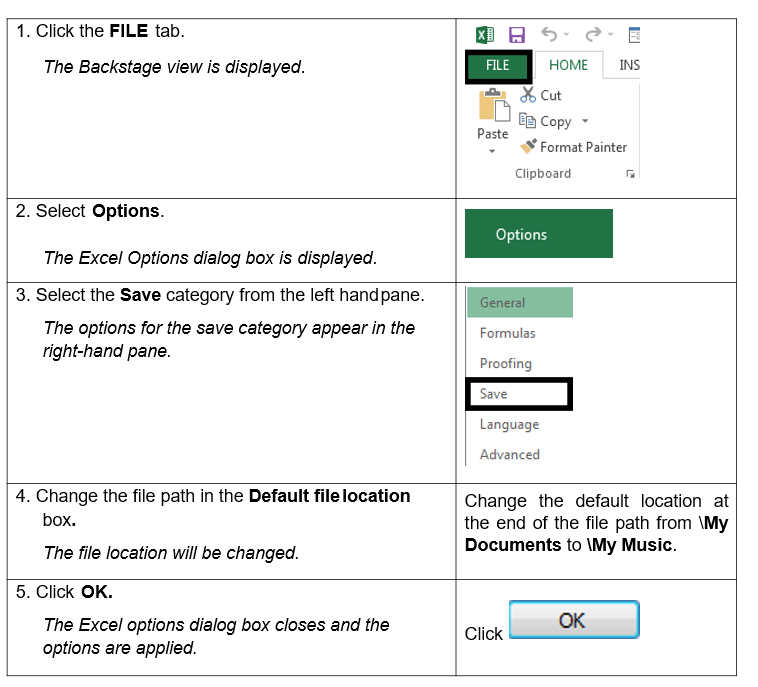
1.1. CREATING A WORKBOOK
Concepts
A Microsoft Office Excel workbook is a file that contains one or
more worksheets that you can use to organize various kinds of related information. You can create a new workbook by simply opening a blank one. You can also use templates on which to base the new workbook, such as the default template provided with Microsoft Excel or templates you have created
Steps
To create a new blank workbook
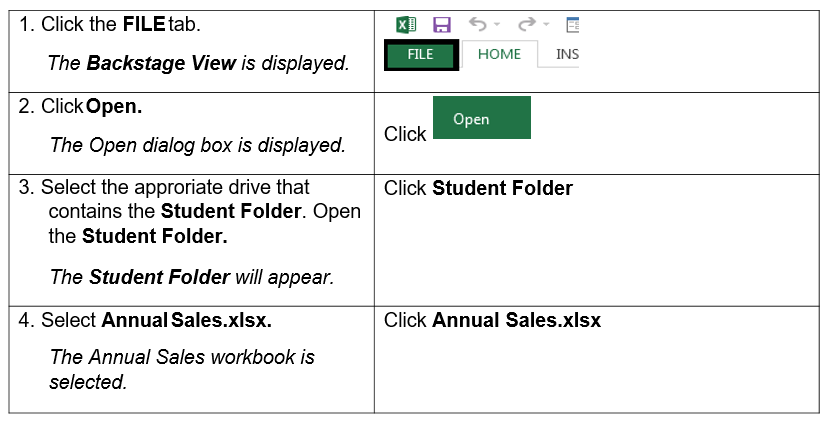
1.2. OPENING A WORKBOOK
You can open an existing workbook to work on in Excel instead of always starting with a blank workbook. The workbook may be on a storage device, cloud service, or an online application.
Steps
Open an existing workbook from a specific drive and folder location. Open a blank workbook.
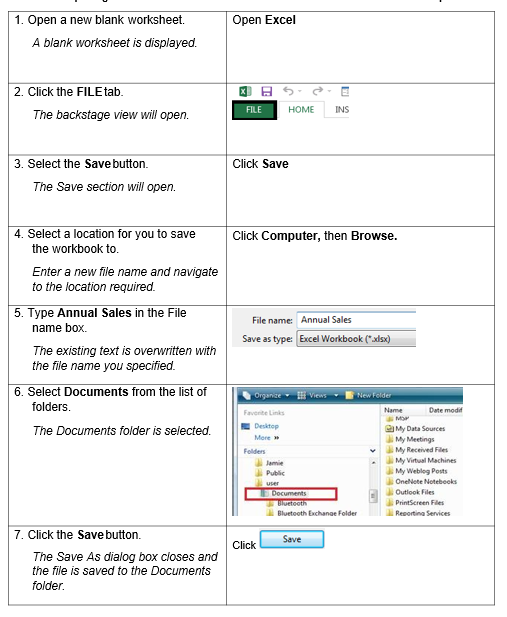
1.3. SAVING A NEW WORKBOOK
Whether using the desktop or web version of Excel, you save documents through the FILE tab, no matter where you wish to save the document to.

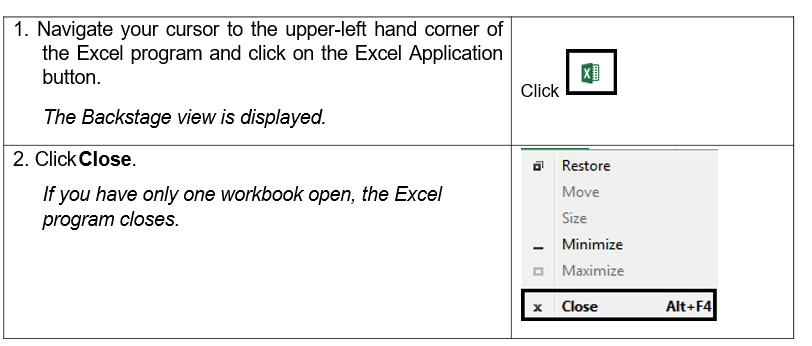
1.4. CLOSING A WORKBOOK
Steps
To close a workbook:
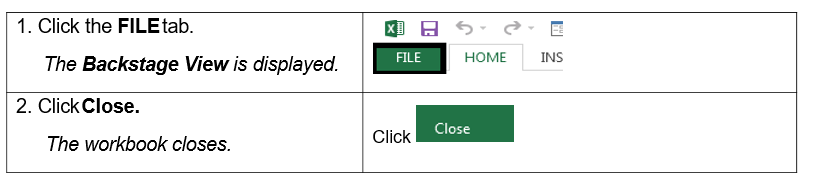
If a message box opens, asking you if you want to save the workbook, click Don’t save.
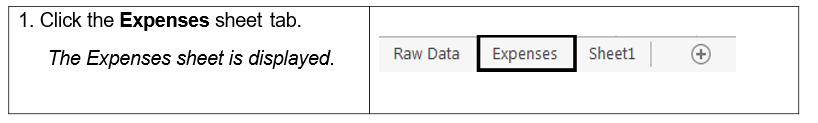
1.5. WORKING WITH WORKSHEETS
The tab at the bottom of a worksheet displays the name of the worksheet - such as Sheet1, Sheet2, etc. You can switch between worksheets by selecting the desired tab. You can add, rename, and move tab positions as shown in the steps below.
Steps
To work with worksheets:
Open Explore.xlsx. Notice the worksheet tabs at bottom of the Excel window.
You can quickly insert a new worksheet by clicking on the button. Excel named these worksheets using a default name, so consider renaming your worksheets to reflect what they contain. To rename it, double-click on the existing sheet name (e.g. Sheet1) and type a new name.
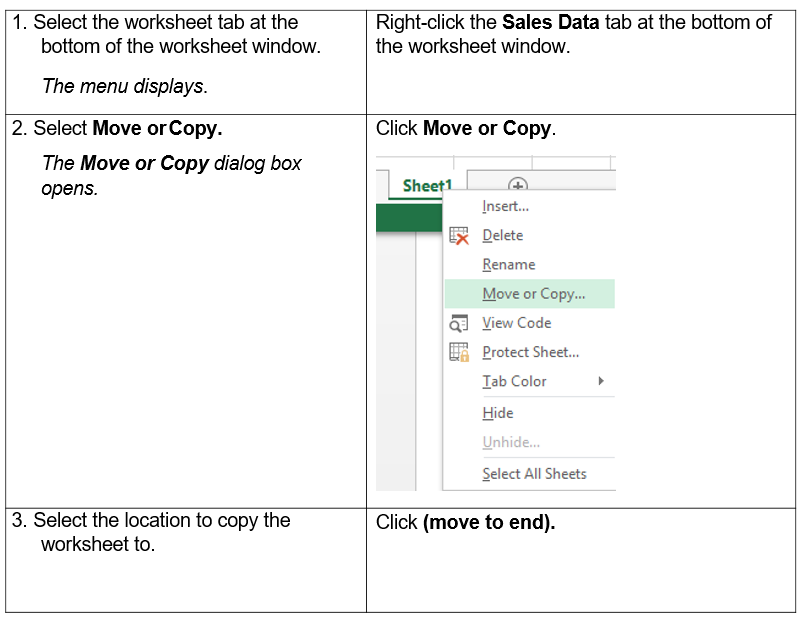
You can copy and move a worksheet within a spreadsheet by right-clicking the worksheet at the bottom of the workbook window, clicking Move or Copy, selecting the location to move the worksheet too, and clicking OK.
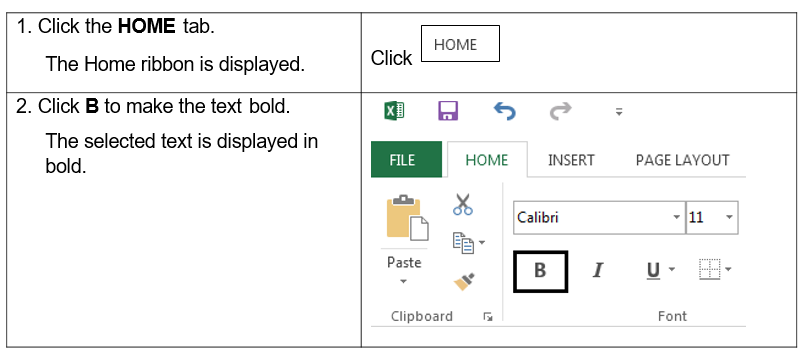
1.6. USING THE RIBBON
The Ribbon is designed to help you quickly find the commands that you need to complete a task. Commands are organized in logical groups, which are collected together under tabs. Each tab relates to a type of activity, such as writing or laying out a page. To reduce clutter, some tabs are shown only when needed. For example, the Picture Tools tab is shown only when a picture is selected.
Steps
Using the ribbon to make the text
bold
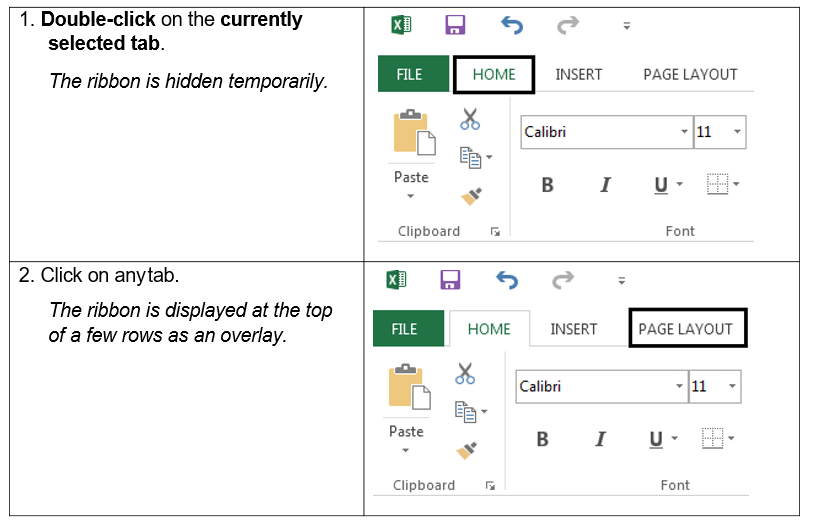
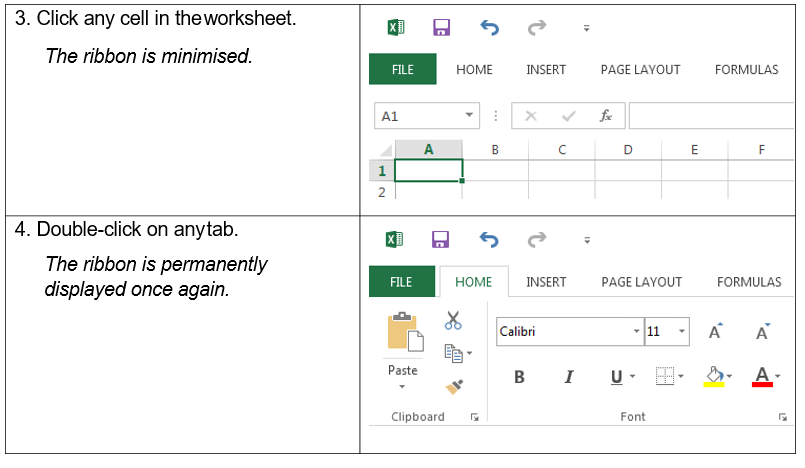
HIDING THE RIBBON
You can’t delete or replace the
Ribbon with the toolbars and menus from the earlier
versions of Microsoft Office, although
you
can
minimize
it to allow
for more on-screen
space. When
this option
is in use, the
ribbon
reappears when you click on a tab, then disappears after
you
select
a command or when
you
click anywhere in the
worksheet
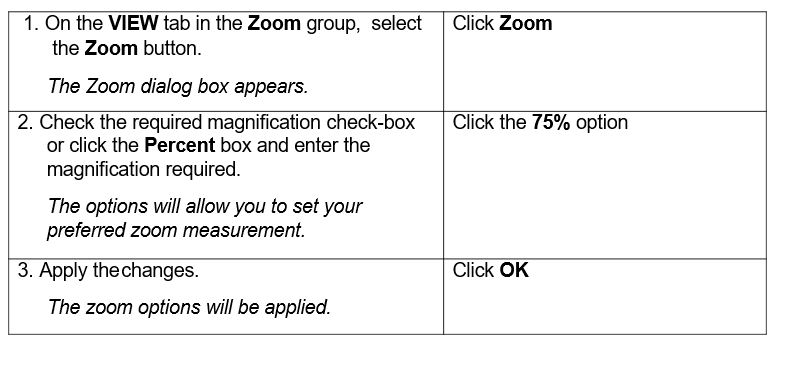
1.7. USING MAGNIFICATION/ZOOM TOOLS
You can use the magnification/zoom tools to display the book depending on your needs.
1.8. CLOSING AND EXITING EXCEL
When you’re ready to quit Excel, you have several choices for shutting down the program:
Be sure to save your changes before exiting the workbook you’ve been working on. If you attempt to leave the workbook without saving it, an alert box appears in Excel warning you that your changes will not be saved. To save these changes before exiting click the Save button. If you don’t want to save your changes click Don’t Save.
Steps
To exit Excel: